Ever felt like you're shouting your event details into an online void? You're not alone. This is exactly where event schema markup steps in. Think of it as a special code that acts as a universal translator, turning your event info - dates, locations, ticket links - into a language search engines like Google instantly get. It’s like giving your event a VIP pass straight to the top of the search results.
Why Event Schema Is a Game-Changer for Your SEO
Simply put, event schema is a form of structured data that tells search engines exactly what your page is about. Instead of making Google guess, you’re explicitly saying: "Hey, this page is about a concert. It's happening on this date, at this venue, and here's the link to buy tickets."
This kind of direct communication is incredibly powerful. It makes your event eligible to be featured in what are called rich results - those eye-catching, detailed listings that practically jump off the search results page.
The Power of Visibility and Rich Results
When you implement event schema, you're not just whispering details to search engines; you're setting your event up for some serious special treatment. This can look like:
- Prime Real Estate: Your event can land in special carousels or info boxes right at the top of the search results.
- Instant Answers: Key details like date, time, and location are displayed directly, giving users what they need without a click.
- More Clicks: Rich results are just more visually appealing. They offer more value upfront, which almost always translates to a higher click-through rate.
Using event schema markup is one of the most direct and effective strategies for how to rank higher on Google, especially for local searches and specific event queries.
Key Takeaway: Event schema isn't just a technical tweak. It's a core part of modern event marketing that turns a plain webpage into a dynamic, interactive listing that grabs attention and drives people to show up.
This structured data is all part of the much larger Schema.org vocabulary, a joint effort kicked off back in 2011 by Google, Bing, and Yahoo. Fast forward to 2024, and this shared language has ballooned to include 811 different types of markup. It's not a niche trick, either - nearly 23% of all active websites use some form of it.
For anyone promoting an event, this means there's a standardized, widely accepted way to describe everything from a huge festival to a small local workshop. By applying this code correctly, you turn a passive event listing into an active signal for search engines, seriously boosting your discoverability and helping you connect with a much bigger audience.
Getting Started With Your First Event Schema Markup
Diving into your first event schema markup might sound overly technical, but it’s a lot more straightforward than you’d think. The most common - and best - format to use is JSON-LD. It’s just a clean script you pop into the <head> section of your webpage. The beauty of it is that it’s completely self-contained, and Google prefers it.
Let's walk through a real-world example to make this tangible. Imagine you're promoting a local music gig. You want to feed search engines all the critical details so they can showcase your event properly. The code itself is really just a collection of "property: value" pairs that paint a picture of the event.
Laying the Foundation
Every event schema starts with a few non-negotiable properties. These are the absolute must-haves that form the skeleton of your markup. Think of them as the classic "who, what, when, and where" for your event.
You’ll always need to define these core elements:
- @type: This is your first declaration, telling Google you're describing an "Event."
- name: The official title, like "Summer Solstice Indie Fest." Keep it consistent with what’s on the page.
- startDate: The date and time the event kicks off, formatted in ISO 8601 (e.g., "2024-09-15T19:00:00-05:00").
- location: Where the event is happening. This is actually a nested property with its own details, like the venue's name and address.
Here’s what that basic JSON-LD snippet looks like when you're putting it together.
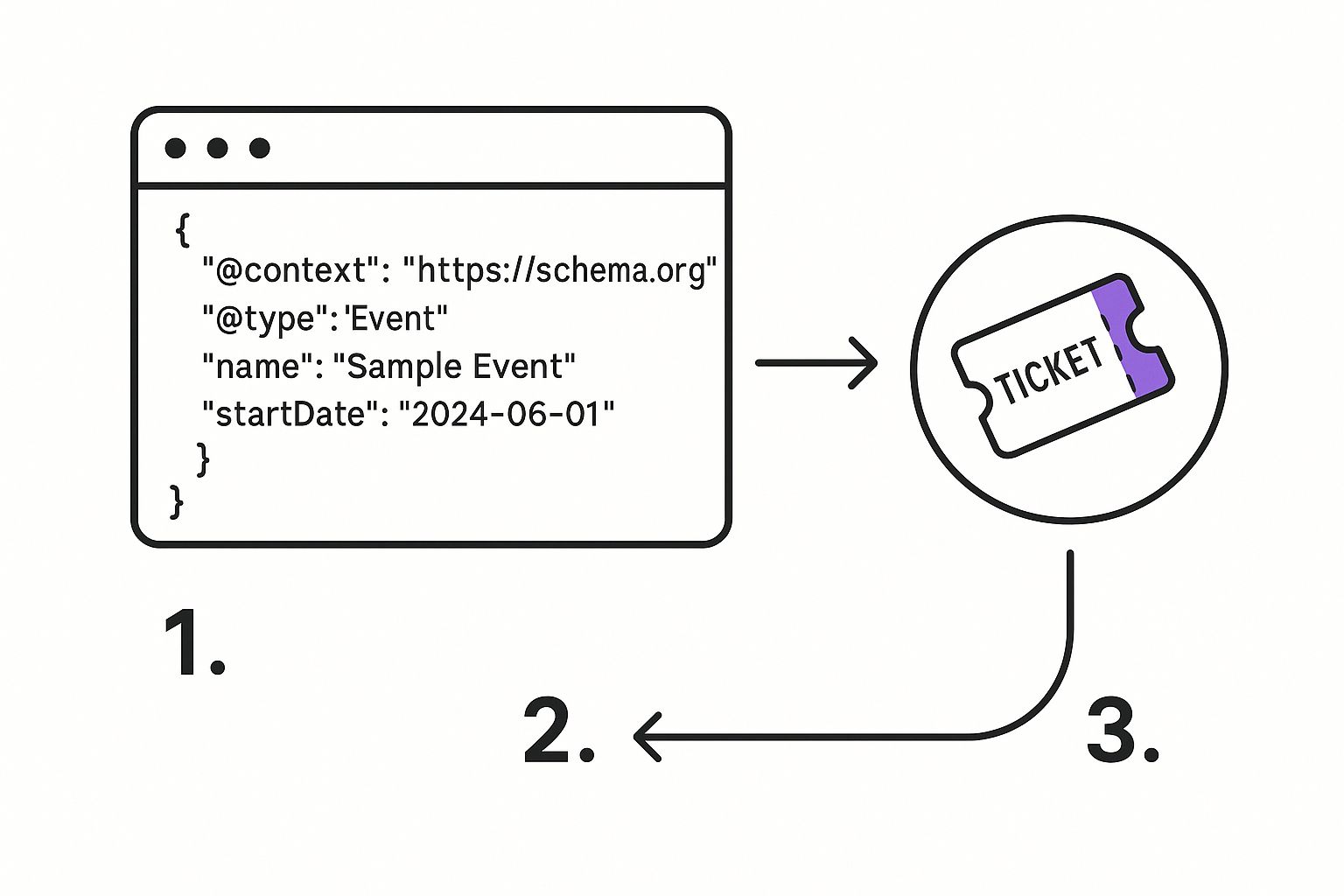
As you can see, these key-value pairs create a simple, structured summary that machines can easily digest.
Adding Richer Details
Once you have the basics down, you can start layering in more details to make your listing even more compelling for potential attendees. This is the information that really helps your event stand out from the crowd.
Consider including properties like:
- performer: Specify the artist, band, or speaker.
- offers: This is where you list ticket prices, availability, and a direct URL to the purchase page.
- description: A short, punchy summary of what makes your event special.
The adoption of schema markup has exploded for a simple reason: it makes web content crystal clear to search engines. Research analyzing 10 billion web pages found that 31.3% had adopted some form of Schema.org markup - that's a 42% jump from the previous year. What's more, each marked-up page on average defines six distinct entities. This creates a rich, connected web of data that dramatically improves how content is understood. You can read more about these findings on how schema enriches web content.
A Quick Tip: It's incredibly important to always make sure the information in your schema perfectly matches the content visible to users on the page. Any discrepancies can confuse search engines and might even lead to penalties. It's a simple check that saves a lot of headaches.
The properties you choose will naturally change based on the event type. A recurring virtual meetup, for example, would look different from a one-off conference. For the meetup, you'd set the eventAttendanceMode to OnlineEvent and could even use a repeatFrequency property. For the conference, you'd likely focus on a detailed location and list out all the speakers under the performer property.
Ultimately, crafting clean and accurate event schema markup is your direct line of communication with search engines. It gives you a surprising amount of control over how your event shows up to the world.
Validating Your Schema to Ensure It Works
So you've put in the work and crafted your event schema. That's a huge step, but the job isn't truly done until you've double-checked that your code actually works the way Google expects it to.
This is where Google's Rich Results Test comes into play. It's your go-to tool for this exact purpose. You can simply paste your code snippet or an entire URL, and it will tell you if your page is eligible for those eye-catching rich results. It's the fastest way to see if your markup is valid or if something is holding you back.
Using Google's Validation Tools
Google gives us two main tools for checking structured data: the Rich Results Test and the Schema Markup Validator. They sound similar, but they have slightly different jobs.
- Rich Results Test: This is your primary tool. It looks at your code from one perspective: is it good enough for Google's rich results? It's all about eligibility for things like an event listing in search.
- Schema Markup Validator: This tool, found over at schema.org, is a bit more academic. It validates your code against the entire Schema.org vocabulary, not just what Google needs for a rich result.
Our advice? Always start with the Rich Results Test. It cuts straight to the chase and tells you if your event schema markup meets the specific standards Google has for getting that extra visibility.
Interpreting Errors and Warnings
When you run a test, you'll get one of three results: valid, valid with warnings, or invalid with errors. Knowing how to read these is key to fixing things efficiently.
Key Insight: An 'error' is a showstopper. It means your schema is broken and your page is not eligible for rich results until it's fixed. A 'warning' is more of a suggestion for improvement; your page is still eligible, but you could enhance the markup with recommended (but not required) properties.
Common errors are often simple typos or formatting mistakes, like getting the ISO 8601 date format wrong. Missing a required property like location or name will also throw an error. Warnings, on the other hand, might point out that you're missing recommended fields like performer or offers.
Always fix the errors first. Then, circle back and address the warnings to make your markup as complete and powerful as possible.
This validation step isn't just for big enterprise teams. Recent data shows that a surprising 40% of people implementing schema work at tiny companies with fewer than five people. It just goes to show that getting structured data right is a fundamental skill for marketers at businesses of all sizes. If you're curious, you can discover more insights on the state of schema markup and see how your work stacks up.
Best Practices for Impactful Event Schema
Going beyond the basic required fields is what separates so-so event schema from markup that genuinely moves the needle. To really get the most out of your efforts, you need to think like a search engine and paint the clearest, most complete picture of your event.
A classic scenario we see is managing an event with a last-minute change. Say a concert gets postponed or a webinar has to be rescheduled. Your first instinct might be to just delete the old date, but that's a mistake. Instead, you should use the eventStatus property. Set it to EventPostponed or EventCancelled. This simple update keeps everyone - search engines and potential attendees - in the loop, preventing frustration and protecting the SEO value you've already built.
Handling Different Event Formats
Your schema strategy needs to be flexible. The way you mark up a local meetup is completely different from how you'd handle a global virtual summit. Not all events are simple, in-person gatherings, and your code needs to reflect that reality.
Think about these common event types:
- Virtual Conferences: For any online-only event, you absolutely must set the
eventAttendanceModetohttps://schema.org/OnlineEvent. From there, use thevirtualLocationproperty to add the specific URL where people will actually join the event. - Recurring Workshops: If you're running a workshop every week or month, don't spin up a dozen separate event pages. That's a management nightmare. Instead, use a single event schema and tell Google it's a recurring event with the
repeatFrequencyproperty. - Hybrid Events: Got an event with both physical and virtual attendance? No problem. You can specify both an
OnlineEventand anOfflineEventwithin the same schema structure. This covers all your bases and makes sure you show up for both "in-person" and "online" searches.
Nailing these formats is how you get found. It ensures that when someone searches for something specific - like "online marketing workshops" - your perfectly marked-up event is a top contender.
A Quick Note on Cleanliness: One of the most important habits to get into is nesting your properties correctly. Don't just list a flat address. Instead, nest
streetAddress,addressLocality, andpostalCodeinside aPostalAddresstype, which then lives inside the mainlocationproperty. The same logic applies to youroffers. This clean, hierarchical structure is much easier for search engines to parse and understand.
Avoid Common Pitfalls
While rich, detailed schema can be a massive boost, getting it wrong can actually hurt you. Here's the number one rule you can't forget: your structured data must match the content visible on the page.
Never add information to your schema that a user can't also see on the page. Search engines view this as a spammy, deceptive tactic, and it could land you a penalty.
For example, don't put a price in your schema if that price isn't clearly displayed on the page. And definitely don't mark up a "sold out" event as InStock. These little discrepancies destroy trust with both users and search engines.
Ultimately, great schema is just one piece of the puzzle. A truly effective promotional strategy combines on-page content, social media buzz, and technical SEO like this. When you put it all together in a solid event marketing plan, you create a powerful engine for driving attendance. By following these best practices, your schema will be robust, honest, and incredibly effective at connecting you with your perfect audience.
Streamlining Schema with Add to Calendar PRO
While you can absolutely write JSON-LD by hand, let's be honest - it can be tedious. One misplaced comma or an incorrect date format can break your entire event schema. This is where a little automation doesn't just help; it completely changes the game.
Our service, Add to Calendar PRO, was built to fix this exact headache. Its primary function is creating universal 'Add to Calendar' buttons, but a key benefit is that it automatically generates the required JSON-LD event schema for you. You never have to touch a single line of code.
This means your schema is always right and always up-to-date. When you create an event in our system, the correct, error-free markup gets generated in the background, ready for search engines to find.
Saving Time and Eliminating Technical Headaches
Manually wrangling event schema can eat up a surprising amount of your time, especially if you're dealing with anything more complicated than a simple one-off event. We designed our service to handle all those fussy details, so you can get back to the creative side of promoting your event.
Here’s how it makes life easier:
- Time Zone Conversions: Our system manages all the time zone and daylight saving adjustments automatically. This ensures the
startDateandendDatein your schema are always spot-on for a global audience. - Multi-Day Schedules: Got a multi-day conference or a week-long festival? Just set the start and end dates. Our service will structure the schema correctly without you needing to do anything extra.
- Updates and Changes: If an event gets postponed or details change, you only have to update it once in our dashboard. The schema markup updates on its own, instantly reflecting the new information.
Our Take: We believe technical SEO shouldn't be a roadblock for great event marketing. By building valid event schema generation right into our service, we take the technical weight off your shoulders. This lets marketers and event organizers get all the SEO benefits without needing to become developers.
How It All Works Together
The process is refreshingly simple. You enter your event details - name, date, location, description - into our easy-to-use interface to create your 'Add to Calendar' button. As you're doing this, our service is simultaneously building a complete, valid JSON-LD script on the backend.
This script includes every property Google needs to understand your event, from the basics like name and location to more advanced details like eventStatus and organizer. This two-for-one approach handles both user engagement (with the calendar button) and search engine visibility (with the schema) in one go.
This is especially useful for teams using content management systems. For instance, many WordPress event plugins work great alongside our service, letting you build a really powerful marketing stack. Many of our users also find that pairing our tool with RSVP functionality creates a complete system for managing attendance. It's even possible to create an RSVP link that works seamlessly with your event listings.
Manual Schema vs. Add to Calendar PRO Integration
To put it all in perspective, here's a quick comparison of what it takes to implement schema manually versus letting our service handle it.
| Feature | Manual Implementation | Add to Calendar PRO |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup | Requires coding knowledge (JSON-LD), manual data entry, and careful syntax checking. | No coding needed. Just fill out a simple form with your event details. |
| Accuracy | High risk of human error (typos, incorrect formats) that can invalidate the entire schema. | 100% accurate and valid JSON-LD generated automatically based on your input. |
| Time Investment | Can be time-consuming, especially for recurring or complex events. | Minimal. An event can be set up with schema in just a few minutes. |
| Event Updates | Requires manually finding and editing the code for every change, risking new errors. | Update your event once in the dashboard, and the schema updates instantly and automatically. |
| Advanced Features | Implementing properties like organizer, performer, or offers requires more complex coding. | All relevant properties are included automatically based on the details you provide. |
At the end of the day, while manual implementation gives you control, it comes with a significant cost in time and potential for errors. Our automated approach gives you the same SEO benefits without the technical hassle.
Ultimately, by letting our service handle the technical side of event schema markup, you ensure you’re following best practices and save yourself a ton of valuable time - time better spent actually connecting with your audience.
Common Questions About Event Schema Markup
Even after you've got the basics down, a few questions always seem to pop up. It's completely normal. As a team that lives and breathes events, we've seen just about every query from marketers and developers trying to get their event schema markup perfect.
So, let's tackle some of the most common ones we hear. The goal here is to give you that last bit of clarity you need to move forward with confidence, fix any nagging issues, and really get the hang of this powerful SEO tool.
Event vs. ScreeningEvent: What Is the Difference?
One of the first hurdles people run into is choosing between the general Event type and its more specific cousins. A perfect example is ScreeningEvent.
Event: Think of this as your all-purpose workhorse. It’s a great fit for almost any kind of gathering, from a business conference to a community bake sale.ScreeningEvent: This one is super specific. It's designed only for film or television screenings.
So, when do you use which? The best practice is always to be as specific as you possibly can. If you're promoting a film festival, using ScreeningEvent is much better than the generic Event. That extra detail helps search engines categorize your content more accurately and can even unlock special rich results, like showing movie posters or critic ratings right on the search page.
Can I Use Multiple Schemas on One Page?
Absolutely! In fact, you often should.
Imagine you have a single page listing a whole month's worth of workshops or a full festival schedule. In a case like this, you should create a separate and complete Event schema for each individual event.
The right way to do this is to place each distinct JSON-LD Event object into an array, all inside a single <script> tag. This tells Google, "Hey, this page has a list of unique events," which allows the search engine to identify and maybe even feature each one separately. Trying to cram all your events into a single schema block just won't work.
Our Pro Tip: When an event is over, don't just delete the page! That creates a 404 error and a dead end for users. A much better approach is to update the
eventStatustoEventCompleted. This keeps all that valuable content and SEO juice you've built up.
How Should I Update a Postponed or Canceled Event?
Life happens, and events change. Keeping your schema updated is crucial for user trust and making sure Google has the right information. The key here is the eventStatus property.
All you have to do is change its value to EventPostponed or EventCancelled.
- For postponed events: Make sure you update the
startDateandendDatewith the new dates as soon as you know them. - For canceled events: Keep the page live but switch the status to
EventCancelled. This is so much better than a 404 page because it tells anyone searching for the event exactly what happened.
Keeping people in the loop is also critical after they’ve added an event to their calendar. You can learn more about crafting effective messages by reading our guide on sending email event reminders, which you can easily adapt for status updates.
Does Schema Guarantee a Rich Result?
This is the big one. And the short answer is: No, it does not.
Implementing technically perfect event schema makes your page eligible for rich results, but it’s no guarantee. Google’s algorithms have the final say, and they look at a ton of factors - the search query, the user's location and device, and the overall quality of your website.
Your job is to give Google the best possible signal by providing fantastic content and flawless schema. Think of it like buying a lottery ticket. You have to be in it to win it, but you still need your numbers to be called.
At Add to Calendar PRO, we simplify this entire process by generating flawless event schema automatically, ensuring you're always putting your best foot forward for search engines. Check out our service to see how easy it can be.



